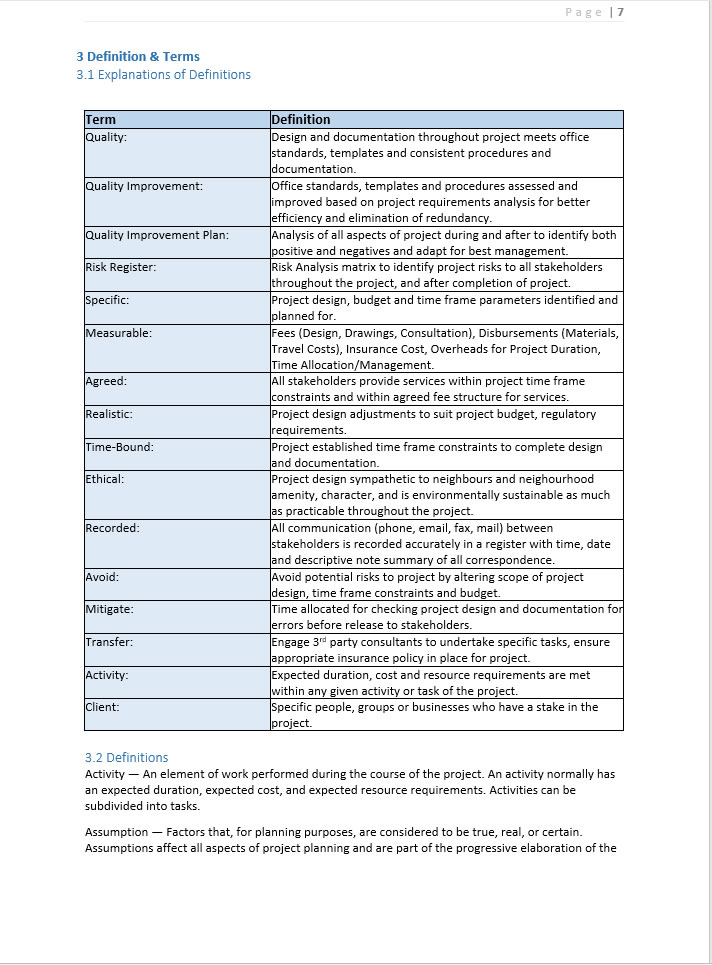
3 Definition & Terms
3.1 Explanations of Definitions
Term |
Definition |
Quality: |
Design and documentation throughout project meets office standards, templates and consistent procedures and documentation. |
Quality Improvement: |
Office standards, templates and procedures assessed and improved based on project requirements analysis for better efficiency and elimination of redundancy. |
Quality Improvement Plan: |
Analysis of all aspects of project during and after to identify both positive and negatives and adapt for best management. |
Risk Register: |
Risk Analysis matrix to identify project risks to all stakeholders throughout the project, and after completion of project. |
Specific: |
Project design, budget and time frame parameters identified and planned for. |
Measurable: |
Fees (Design, Drawings, Consultation), Disbursements (Materials, Travel Costs), Insurance Cost, Overheads for Project Duration, Time Allocation/Management. |
Agreed: |
All stakeholders provide services within project time frame constraints and within agreed fee structure for services. |
Realistic: |
Project design adjustments to suit project budget, regulatory requirements. |
Time-Bound: |
Project established time frame constraints to complete design and documentation. |
Ethical: |
Project design sympathetic to neighbours and neighourhood amenity, character, and is environmentally sustainable as much as practicable throughout the project. |
Recorded: |
All communication (phone, email, fax, mail) between stakeholders is recorded accurately in a register with time, date and descriptive note summary of all correspondence. |
Avoid: |
Avoid potential risks to project by altering scope of project design, time frame constraints and budget. |
Mitigate: |
Time allocated for checking project design and documentation for errors before release to stakeholders. |
Transfer: |
Engage 3rd party consultants to undertake specific tasks, ensure appropriate insurance policy in place for project. |
Activity: |
Expected duration, cost and resource requirements are met within any given activity or task of the project. |
Client: |
Specific people, groups or businesses who have a stake in the project. |
3.2 Definitions
Activity — An element of work performed during the course of the project. An activity normally has an expected duration, expected cost, and expected resource requirements. Activities can be subdivided into tasks.
Assumption — Factors that, for planning purposes, are considered to be true, real, or certain. Assumptions affect all aspects of project planning and are part of the progressive elaboration of the project. Project teams frequently identify, document, and validate assumptions as part of their planning process. Assumptions generally involve a degree of risk.
Client - Specific people, or groups, who have a stake (stakeholder) in the outcome of the project. A project client may be a corporate organisation, developer investors, community groups and government organisation.
Closure phase - The final phase of a project. It usually comprises handover of documentation to tender project works.
Constraint — A known fact that will influence how the project is planned and managed. A constraint is a given factor that is outside the scope of the project leader’s control, which will require project actions to work through the constraint or around it.
Contingency Plan - The identification of alternative means for achieving project objectives, and will usually result in the development of a project risk-management plan that identifies alternatives to be used if and when specified project risk events occur.
Critical Path — The series of activities that determines the duration of the project: the sequence of activities that must be completed on schedule for the entire project to be completed successfully on schedule.
Customer Client - The person(s), group or company that are the direct beneficiary of the project work or service. The entity for whom the project is being undertaken.
Duration - Duration is the amount of time from the beginning of the activity to its completion expressed in days or weeks.
End-user- The individuals who will actually use the outcomes of the project.
Functional - A functional description in the sense states what the project is expected to do or perform - its functionality.
Gantt chart — A spreadsheet graphic display of schedule-related project activities.
Initial phase - The first phase of the project development cycle during which the viability/feasibility of the project is assessed and the project objectives are defined.
Methodology — A project risk management methodology shall be a set of inter-related phases, activities and tasks that define the process from the feasibility of a project through to its completion at tender.
Milestone - A milestone is a scheduling event that signifies the completion of a major project works deliverable or a set of related deliverables.
Network - A network diagram depicts the sequence of the activities from the feasibility stage in an early chronological order as well as the relationships and dependencies between the activities.
Objective - A concrete statement describing what the project is trying to achieve. Objectives shall be specific, measurable, attainable achievable, realistic time bound and agreed.
Planning phase - Follows the initial phase and is where the project is planned in detail. This phase includes all of those activities that further develop and define the components of the project plan.
Post Project Review - Reviews the project processes and their impact on delivery of the project objectives. Post project review shall take place as close as possible to the handover of the project documents.
Project — A set of interrelated activities designed/undertaken to achieve a common/specific goal. A project has a specific begin date and end date, specific objectives and specific resources assigned to perform the work. A Project leader has overall responsibility and authority over the project.
Project Leader - The person with authority to manage the project. This includes leading the planning and the development of all project deliverables. The Project Manager is responsible for managing the budget and Project Schedule and all project risk- management procedures.
Project Phases- Projects may be divided up into phases for monitoring and control. Such phases provide GO/NO GO points at which the project may be terminated or approved to carry on to the next phase. A project may have any number of phases. The number is determined by the needs of the project outlined in the project brief. The usual minimum number of phases is six — feasibility, design concept, design development, documentation, tender, post tender.
Project Plan — This is a formal approved document used to guide both project implementation and project control. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, to facilitate communication among all stakeholders, to achieve a common understanding and to document approved scope, cost, schedule baselines, risk, quality, human resources and procurement requirements.
Project Proposal-The end product of the initial feasibility phase of the project in which the nature of the project is defined. This document formally authorises the existence of the project and it provides the project leader with the authority to apply organisational resources to project activities.
Project purpose -The over-arching reason for creating the project.
Project Team - The project team consists of the full-time and part-time resources assigned to work on the deliverables of the project, which will help achieve the project objectives- The project team are responsible for:
- Understanding the work to be completed
- Planning out the assigned activities in more detail if needed.
- Completing assigned work within the budget, timeline and quality expectations
- Informing the Project Leader of issues, scope changes, risk and quality concerns
- Proactively communicating status and managing expectations
The project team can consist of human resources within Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd, or it can consist of members from many different secondary consultants.
Risk - There may be external circumstances or events that must not occur for the project to be successful.
Risk Management — Risk management is the systematic process of identifying, analysing and responding to project risk. it includes maximising the probability and consequences of positive events and minimising the probability and consequences of events adverse to project objectives.
Schedule - This is the planned dates for performing activities and/or milestones.
Scope - Scope is the way that Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd describes the boundaries of the project. It defines what the project will deliver and what it will not deliver.
Scope Definition - A detailed, itemised statement of what is in the project and may include reference to functionality and quality standards.
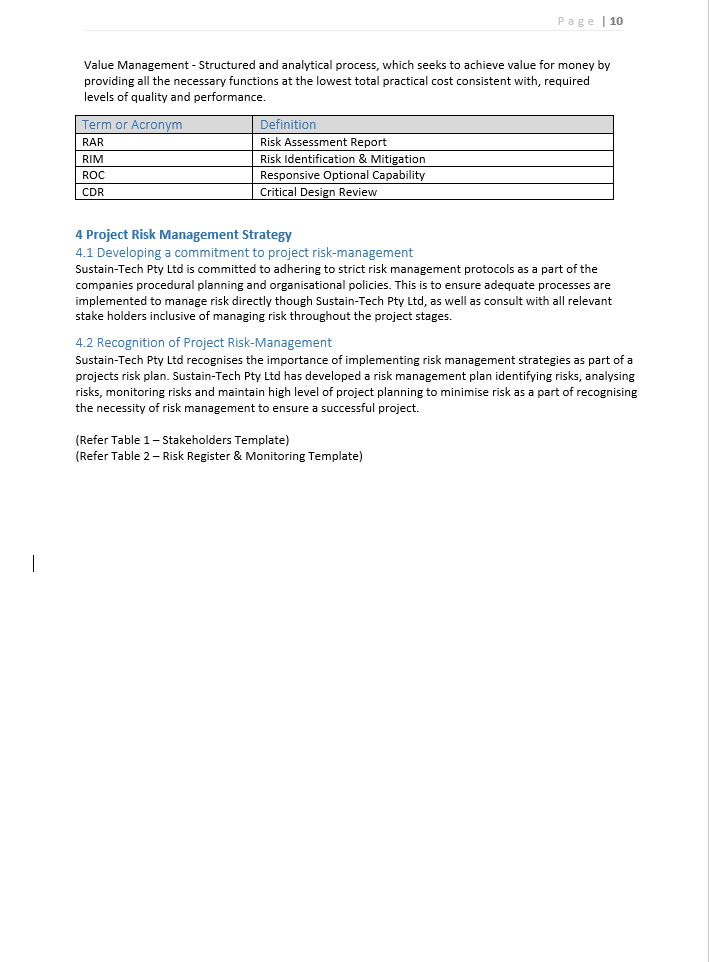
Value Management - Structured and analytical process, which seeks to achieve value for money by providing all the necessary functions at the lowest total practical cost consistent with, required levels of quality and performance.
|
Definition |
RAR |
Risk Assessment Report |
RIM |
Risk Identification & Mitigation |
ROC |
Responsive Optional Capability |
CDR |
Critical Design Review |
4 Project Risk Management Strategy
4.1 Developing a commitment to project risk-management
Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd is committed to adhering to strict risk management protocols as a part of the companies procedural planning and organisational policies. This is to ensure adequate processes are implemented to manage risk directly though Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd, as well as consult with all relevant stake holders inclusive of managing risk throughout the project stages.
4.2 Recognition of Project Risk-Management
Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd recognises the importance of implementing risk management strategies as part of a projects risk plan. Sustain-Tech Pty Ltd has developed a risk management plan identifying risks, analysing risks, monitoring risks and maintain high level of project planning to minimise risk as a part of recognising the necessity of risk management to ensure a successful project.
(Refer Table 1 – Stakeholders Template)
(Refer Table 2 – Risk Register & Monitoring Template)


|






